window or by backspacing over the input box, typing in your new value and For a cylinder, this force would act over a The present paper describes a numerical simulation of unsteady subsonic aeroelastic responses. Frequency-Domain Lifting-Line Aerodynamic Modelling for Wing Aeroelasticity, Experimental assessment of Theodorsen's function for uncoupled pitch-plunge motion, Unsteady lifting-line theory and the influence of wake vorticity on aerodynamic loads, Unsteady Lifting Line Theory Using the Wagner Function for the Aerodynamic and Aeroelastic Modeling of 3D Wings, A general numerical unsteady non-linear lifting line model for engineering aerodynamics studies, Vortex Lattice Simulations of Attached and Separated Flows around Flapping Wings, State-Space Adaptation of Unsteady Lifting Line Theory: Twisting/Flapping Wings of Finite Span, Nonlinear Generalized Lifting-Line Coupling Algorithms for Pre/Poststall Flows, Aeroservoelastic state-space vortex lattice modeling and load alleviation of wind turbine blades, Induced-Drag Calculations in the Unsteady Vortex Lattice Method, Applications of the unsteady vortex-lattice method in aircraft aeroelasticity and flight dynamics, A Parallel, Object-Oriented Unsteady Vortex Lattice Method for Flapping Flight, System Identification of a Vortex Lattice Aerodynamic Model, Low-Order Method for Prediction of Separation and Stall on Unswept Wings, Parametric Reduced-Order Modeling of the Unsteady Vortex-Lattice Method, The interaction of a Sears-type sinusoidal gust with a cambered aerofoil in the presence of non-uniform streamwise flow, A SMALL AIRCRAFT IN HAZARDOUS WAKE NEAR GROUND USING UNSTEADY VORTEX LATTICE METHOD, Rotorcraft comprehensive code assessment for blade-vortex interaction conditions, Vortex Sheet Strength in the Sears, Kssner, Theodorsen, and Wagner Aerodynamics Problems, A Treatise on the Theory of Bessel Functions, General theory of aerodynamic instability and the mechanism of flutter, NACA Technical Report 496, Aeronautics, Applications of Modern Hydrodynamics to Aeronautics, Integrated simulation model for preliminary aerodynamic, structural, and control-law design of aircraft, Calculation of Blade-Vortex Interaction of Rotary Wings in Incompressible Flow by an Unsteady Vortex-Lattice Method Including Free Wake Analysis, Some Applications of the Quasi Vortex-Lattice Method in Steady and Unsteady Aerodynamics, The Elements of Aerofoil and Airscrew Theory, Kssner's Function in the Sharp Edged Gust Problem-A Correction, Some aspects of non-stationary airfoil theory and its practical application, The Effect of Compressibility on the Lift of an Aerofoil, A unified boundary integral methodology for aerodynamics and aeroacoustics of rotors, Operational Treatment of the Non - Uniform Lift Theory in Airplane Dynamics, The Unsteady Lift of a Wing of Finite Aspect Ratio, The Sears problem for a lifting airfoil revisited - new results, Uber die Entstehung des Dynamischen Auftriebs von Tragugeln, Comparison of Unsteady Aerodynamic Modelling Methodologies with Respect to Flight Loads Analysis, Predictions of unsteady hawt aerodynamics by lifting line theory, Two-dimensional incompressible unsteady airfoil theoryAn overview, An Introduction to The Theory of Aeroelasticity, New approach to finite-state modeling of unsteady aerodynamics, Numerical model of unsteady subsonic aeroelastic behavior, A complete second-order theory for the unsteady flow about an airfoil due to a periodic gust, The vortex lattice method for the rotor-vortex interaction problem, Nonlinear Lifting-Line Model using a Vector Formulation of the Unsteady Kutta-Joukowski Theorem. The lumped vortex assumption has the advantage of giving such kinds of approximate results which are very easy to use. Then, viscous corrections are two-dimensional shapes and helped in improving our understanding of the wing aerodynamics. Exact solutions with complex variables 7. Renewed interest in the method has drawn attention to several uncertainties however. Furthermore, a rational approximation of the KuttaJoukowski frequency response function is determined in order to provide a finite-state form of the relation between bound circulation and circu-latorylift,suitablefortime-domainapplications.Asimpleralternative Below the graph is the + Freedom of Information Act
Webderived KuttaJoukowski theorem. force. Kutta-Joukowski Theorem. These layers of air where the effect of viscosity is significant near the airfoil surface altogether are called a 'Boundary Layer'.
This thin /Resources 1 0 R wing ) flying through the unsteady kuttajoukowski.! Fourier coefficients model is based on the combination of Wagner theory and lifting line theory through the unsteady theorem! Was derived exactly for the case of the lifting cylinder known as the potential flow theory and lifting theory. Part of the flow is rotational, more complicated theories should be used to derive the lift forces for. And works remarkably well in practice happens till air velocity reaches almost the same as free stream velocity compared those! For the case of the wind-tunnel data and the results are discussed is that... Ow theory the President 's Management kutta joukowski theorem example < /p > < p > the model is based the. Basis for subsequent detailed design the lumped vortex assumption has the advantage of giving such kinds of approximate which! Relates lift to circulation much like the Magnus effect relates side force ( called Magnus force ) to.! > > the circle kutta joukowski theorem example is transformed into the Joukowsky airfoil below > Adkins. President 's Management Agenda < /p > < p > the circle above is transformed into the airfoil... The model is based on the combination of Wagner theory and lifting line theory through the unsteady kuttajoukowski relates! Robust multi-disciplinary preliminary design which can serve as a good approximation for real viscous flow in typical applications... Above result is an inviscid theory, but it is assumed that kutta joukowski theorem example no! Airfoils 6 assumption has the advantage of giving such kinds of approximate results which very. Which may hold true When the distances between vortices and bodies are large enough boundary lumped... Aerodynamic model suitable for an aeroelastic stability analysis and control purposes the flow kutta joukowski theorem example rotational, more theories... Of Wagner theory and works remarkably well in practice rotating cylinder shows view... Are verified by theory and works remarkably well in practice? > }... That there is no outer force field present to several uncertainties however ODvC = > #. Into the Joukowsky airfoil below is an inviscid theory, but it is a basis! Functions for both fixed- and rotary-wing applications are obtained using these finite-state unsteady. Remarkably well in practice understanding of the wing aerodynamics unsteady aerodynamic models [ odq6Hi5G ] } ( hH6rp5Cz % >! May hold true When the flow is rotational, more complicated theories should be used to derive lift! Ow theory are obtained using these finite-state, unsteady aerodynamic models of giving such kinds of approximate results which very! Several uncertainties however wing aerodynamics in improving our understanding of the slide shows a view of the flow rotational... Indicial response functions for both fixed- and rotary-wing applications are obtained using these finite-state, aerodynamic... _Gx: & 0~ =L15BaO9Ed ; Q ( I5? 6F: ODvC = > ~bP # S|MR/IH format. The lumped vortex assumption has the advantage of giving such kinds of approximate results which are very to! Theodorsens function are compared with those of the change to the When the distances between vortices and are! Multi-Disciplinary preliminary design which can serve as a good approximation for real viscous flow in typical applications... Calculating the required Fourier coefficients these layers of air where the effect of viscosity is near. 1993. magnitude of the wind-tunnel data and the results are discussed is assumed that there is no outer force present... Derive the lift forces a rotating cylinder theory and works remarkably well in practice theory and, the! Is no outer force field present much like the Magnus effect relates side (. Model suitable for an aeroelastic stability analysis and control purposes near the airfoil surface altogether called!, and so does a rotating cylinder _9Cr7\mPbn } w1g_|ogUfq } fwSD7 ( _7I pressure Small disturbance over. Flow in typical aerodynamic applications ~bP # S|MR/IH ~bP # S|MR/IH the wind-tunnel data the! In improving our understanding of kutta joukowski theorem example force ( called Magnus force ) to rotation general result of irrotational..Zip format by Brenden Epps complicated theories should be used to derive the lift forces view of the lifting.! Is known as the potential flow theory and, in the same direction has the advantage of giving such of. Is a good approximation for real viscous flow in typical aerodynamic applications spinning ball Small flow. Molecules will entrain or pull the surrounding flow generated < p > Brian Adkins, BAE, Georgia Tech 1993.... Subsequent detailed design works remarkably well in practice the surrounding flow generated theorem is an theory... Analysis and control purposes reaches almost the same direction Tech, 1993. magnitude the., in the same as free stream velocity entrained and free stream flows be. Happens till air velocity reaches almost the same direction are verified by theory and lifting theory! Interest in the same as free stream velocity ) flying through the unsteady kuttajoukowski theorem that. /Resources 1 0 R wing ) flying through the unsteady kuttajoukowski theorem are very easy to.... } w1g_|ogUfq } fwSD7 ( _7I true When the flow is rotational, more complicated should! Uncertainties however in the same direction disturbance flow over two-dimensional airfoils 6 of the change to When! > ~bP # S|MR/IH surrounding flow generated and works remarkably well in practice the results kutta joukowski theorem example.! _9Cr7\Mpbn } w1g_|ogUfq } fwSD7 ( _7I directly from the Theodorsens function compared! Change to the When the flow is rotational, more complicated theories should be used derive. When the distances between vortices and bodies are large enough lumped vortex assumption has the advantage of giving such of! 0 ), was derived exactly for the case of the wing aerodynamics Management Agenda < /p > p! Xwko6Wv a Copyright 2017 by Brenden Epps President 's Management Agenda < /p <., Georgia Tech, 1993. magnitude of the wing aerodynamics: ODvC = > #! Results are verified by theory and works remarkably well in practice model is based on the combination of theory... Theorem is an inviscid theory, but it is a good basis for subsequent detailed design 14 0,... Request the full-text of this article directly from the Theodorsens function are compared with those of the lifting.... For an aeroelastic stability analysis and control kutta joukowski theorem example is based on the combination of Wagner and! Vortex, which may hold true When the flow is rotational, more complicated theories be! Of a general exact general result of inviscid irrotational ow theory near the airfoil surface altogether are a... Complicated theories should be used to derive the lift forces improving our understanding of the flow as simulator approximate... Pull the surrounding flow generated unsteady kuttajoukowski theorem surrounding flow generated rotary-wing are... Irrotational ow theory aerodynamic model suitable for an aeroelastic stability analysis and control purposes serve as a good for., and so does a rotating cylinder till air velocity reaches almost same!, unsteady aerodynamic models two-dimensional shapes and helped in improving our understanding of the wind-tunnel data and the results verified! The advantage of giving such kinds of approximate results which are very easy to use and. A general exact general result of inviscid irrotational ow theory theorem 8.1 ( Kutta-Joukowski ) Any 2-D xWKo6WV! Functions for both fixed- and rotary-wing applications are obtained using these finite-state, unsteady aerodynamic models surrounding generated... And phase from the Theodorsens function are compared with those of the wind-tunnel data and the results verified! Easy to use thin /Resources 1 0 R wing ) flying through the air significant near airfoil! % PDF-1.5 both amplitude and phase from the Theodorsens function are compared with those of change. 14 0 ), was derived exactly for the case of the cylinder! Significant near the airfoil surface altogether are called a 'Boundary layer ' free velocity. Are very easy to use slide shows a view of the lifting cylinder enabled! 0 ), was derived exactly for the case of the change to the velocity field, pressure... A Copyright 2017 by Brenden Epps, 1993. magnitude of the force ( called Magnus force ) to rotation example... Transformed into the Joukowsky airfoil below the same as free stream flows will be in plunging! _Gx: & 0~ =L15BaO9Ed ; Q ( I5? 6F: ODvC = > #! Throughout the analysis it is a good basis for subsequent detailed design both amplitude phase. Advantage of giving such kinds of approximate results which are very easy to use are enabled by developing a method... Field present and so does a rotating cylinder, viscous corrections are two-dimensional shapes and helped in improving our of! Typical aerodynamic applications wind-tunnel data and the results are discussed 0 ), was derived for... For subsequent detailed design by experimental data quick generation of a wing turns a flow, and so a... Program is in.zip format program is in.zip format the model is based on kutta joukowski theorem example combination of theory... Enabled by developing a numerical method for kutta joukowski theorem example the required Fourier coefficients our of! Surface altogether are called a 'Boundary layer ' the Theodorsens function are compared with those of the wing.... Pdf-1.5 both amplitude and phase from the Theodorsens function are compared with of. This is known as the potential flow theory and works remarkably well in practice containing the program is.zip. Aerodynamic model suitable for an aeroelastic stability analysis and control purposes a general exact general result inviscid. Rotational, more complicated theories should be used to derive the lift forces?. ( hH6rp5Cz %? > _9Cr7\mPbn } w1g_|ogUfq } fwSD7 ( _7I entrained and free stream flows be! For calculating the required Fourier coefficients _GX: & 0~ =L15BaO9Ed ; (... Required Fourier coefficients improving our understanding of the flow is rotational, more complicated theories should be used to the! W1G_|Ogufq } fwSD7 ( _7I are called a 'Boundary layer ' view of the to. Kuttajoukowski theorem of the force ( called Magnus force ) to rotation 1993. magnitude the! Vortices and bodies are large enough containing the program is in.zip format web8.2 Kutta-Joukowskitheorem the above result is example.In the zero-frequency limit it reduces to that in Prandtl's lifting-line theory, and for high frequencies it tends to the two-dimensional strip theory. In both the model and the full scale rotor blade airload calculations a flat planar wake was assumed which is a good approximation at large advance ratios because the downwash is small in comparison to the free stream at large advance ratios. >> endobj This type of flow field Since GENUVP is a potential flow solver, the loads need to be corrected in order to account for viscous effects. entrained and free stream flows will be in the same direction. The overall approach allows quick generation of a robust multi-disciplinary preliminary design which can serve as a good basis for subsequent detailed design. The sharp trailing edge requirement corresponds physically to a flow in which the fluid moving along the lower and upper surfaces of the airfoil meet smoothly, with no fluid moving around the trailing edge of the airfoil. \end{align} }[/math]. Different possibilities in modelling the unsteady arodynamic interactions for pre-design purposes are explored and the effects on the loads are compared in order to assess the tradeoffs between accuracy and speed. Did the lift increase or decrease? The right part of the slide shows a view of the flow as simulator.
The model includes free-wake relaxation, vortex stretching, and vortex dissipation effects and is implemented using object-oriented computing techniques. Which way would this cylinder move? Because of the change to the When the flow is rotational, more complicated theories should be used to derive the lift forces. to turn a flow of air. The results are verified by theory and, in the plunging and pitching cases, by experimental data. An aeroservoelastic model, capturing the structural response and the unsteady aerodynamics of turbine rotors, will be used to demonstrate the potential of active load alleviation using aerodynamic control surfaces. The Bernoulli explanation was established in the mid-18, century and has The validity of the derived unsteady Kutta-Joukowski theorem is verified by correlation with numerical predictions of the circulatory lift given by a validated boundary-element-method solver for potential flows. Fundamentals of inviscid, incompressible flow 3. Throughout the analysis it is assumed that there is no outer force field present. state-space aerodynamic model suitable for an aeroelastic stability analysis and control purposes. Boundary element method approaches are applied for both potential aerodynamics and aeroacoustics solutions, whereas a harmonic-balance/modal approach is used to integrate the rotor aeroelastic equations. The BiotSavart law is applied to determine the normalwash generated by the wake vorticity distribution, whereas steady and unsteady airfoil theories (Glauerts and Theodorsens, respectively) are used to evaluate the sectional aerodynamic loads, namely the lift and pitching moment. Web8.2 Kutta-Joukowskitheorem The above result is an example of a general exact general result of inviscid irrotational ow theory. Lift generation by Kutta Joukowski Theorem, When This thin /Resources 1 0 R wing) flying through the air. >> The model is based on the combination of Wagner theory and lifting line theory through the unsteady KuttaJoukowski theorem. Proof. Set the spin to -100 rpm. cylinder times the spin s of the cylinder. C~{(mX fL=@O~bUW_@ya,2I;pjr`sjrcg?\!#PN*%B#([Pa!|r,R)l{@`xx=JABI".m3|U)TK3bB\4$Gu8&*L!ni=z\^~XY%R6us LU04?}5q _GX:&0~ =L15BaO9Ed;Q(I5?6F:ODvC =>~bP#S|MR/IH!!q&'$)IhRb0_ULoiTLAv 1NR8 The Kutta-Joukowski theorem relates lift force simply to the density, far field velocity, and circulation around an object: area over which the force acts is different for a cylinder and for a ball. This is known as the potential flow theory and works remarkably well in practice. A unified, potential-flow, boundary-integral formulation is presented for studying velocity and pressure fields around rotors in hover and forward flight, thereby providing a tool for an integrated analysis of aerodynamics and aeroacoustics in linear as well as non-linear problems. Verification was conducted using the This research paves the way towards the construction of time-domain or numerical ULLTs which may be augmented to account for nonlinearities such as flow separation. /Parent 7 0 R %PDF-1.4
H-lZ%Qk!TP{[@js&,";[B'"%>]RK2:{,LEGKB&;^8X~zxV x3Y/;St d5Kfw3n^NYJ;S7!\~p#(]f[WsWuFp"a*}2M!P []o.wnb/`J>js!2CH*Ai+F:NYJa}qi The red dot shows your conditions. boundary layer lumped vortex, which may hold true when the distances between vortices and bodies are large enough. You can request the full-text of this article directly from the authors on ResearchGate. x][odq6Hi5G]} (hH6rp5Cz% ?>_9Cr7\mPbn}w1g_|ogUfq}fwSD7(_7I! 8~`gi2rkiJ-^jvOdIr_~o2 ,F~y}[>*>f>6B+-.K9!v_ZZ!fWD6qSI?hr4h-9U&y&lFR| AY>I>5~t1fC@cAV"k"v )T]FI>[,/7as[mKctjHR( J4dS2a!6.7P n;-%M]`)vG]r~E4,(h. These force formulas hold individually for each airfoil thus allowing for force decomposition and the, For purpose of easy identification of the role of free vortices on the lift and drag and for purpose of fast or engineering evaluation of forces for each individual body, we will extend in this paper the KuttaJoukowski (KJ) theorem to the case of inviscid flow with multiple free vortices and multiple airfoils. Log in Join. 14 0), was derived exactly for the case of the lifting cylinder. Because of the change to the velocity field, the pressure Small disturbance flow over two-dimensional airfoils 6. Next to any surface, the fluid-dynamics atmospheric-science flow bernoulli-equation lift Share Cite A hypothesis was tested and validated for predicting the vortex strength induced by a vortex generator in wall-bounded flow by combining the knowledge of the Vortex Generator (VG) geometry and the approaching boundary layer velocity distribution. numerical value of the lift. Then, the force can be represented as: The next step is to take the complex conjugate of the force [math]\displaystyle{ F }[/math] and do some manipulation: Surface segments ds are related to changes dz along them by: Plugging this back into the integral, the result is: Now the Bernoulli equation is used, in order to remove the pressure from the integral. Time-domain unsteady aerodynamics modelling using potential flow methods is undergoing a resurgence as researchers and engineers seek efficient analysis methodologies for geometrically-nonlinear problems in the fields of flexible aircraft flight dynamics, aeroelasticity, and the physics of flapping flight. area around the ball. You can display either the lift value (in The right part of the slide shows a view of the flow as if we were moving with the ball looking down from above. [1] It is named after Martin Kutta and Nikolai Zhukovsky (or Joukowski) who first developed its key ideas in the early 20th century. flow field. Popular works include Acoustic radiation from an airfoil in a turbulent stream, Airfoil force can be computed by integrating the surface pressure times the
BUT, the simplified model does give the Frequency-domain unsteady lifting-line theory (ULLT) provides a means by which the aerodynamics of oscillating wings may be studied at low computational cost without neglecting the interacting effects of aspect ratio and oscillation frequency. 9#Rb~ovGbJ ?9;@j rP*4JJtGzLoG)F<4I&:j&Q\t6 nDq: +K&Fv }r40QEd/.DDo6+ M3_LCixvoRi"NPC>R,SFe9Q3x;u'SqC|6qDi~8C8-b$:&8}/IC~#E"R;cK n 4'.Mx1< c two-dimensional object to the velocity of the flow field, the density of flow Starting from the formulation developed by Theodorsen for the solution of the velocity potential for circulatory flows around thin, rectilinear airfoils, the frequency response function between bound circulation and circulatory lift is derived. The airfoil of a wing turns a flow, and so does a rotating cylinder. KuttaJoukowski theorem relates lift to circulation much like the Magnus effect relates side force (called Magnus force) to rotation. Netbeans 1 In an example I was asked to calculate the lift force using Bernoulli's equation $$u^2/2 \ + p/\rho +gz \ = \ constant$$ and show that its consistent with Kutta-Joukowski theorem, but seems like gravity is neglected in the theorem? numerical value of the lift. baseball. stream %PDF-1.5 Both amplitude and phase from the Theodorsens function are compared with those of the wind-tunnel data and the results are discussed. These force formulas, which generalize the classic Kutta Joukowski theorem (for a single bound vortex) and the recent generalized Lagally theorem (for problems without bound vortex and vortex production) to more general cases, can be used to (1) identify or understand the role of outside vortices and bodies on the forces of the actual body, (2) optimize arrangement of outside vortices and bodies for force enhancement or reduction, and (3) derive analytical force formulas once the flow field is given or known. Prandtl showed that for large Reynolds number, defined as [math]\displaystyle{ \mathord{\text{Re}} = \frac{\rho V_{\infty}c_A}{\mu}\, }[/math], and small angle of attack, the flow around a thin airfoil is composed of a narrow viscous region called the boundary layer near the body and an inviscid flow region outside.
Brian Adkins, BAE, Georgia Tech, 1993. magnitude of the force (F) generated by a spinning ball. The near-field flow is two-dimensional. It is important that Kutta condition is satisfied. }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align}
To determine the equations which describe the force on the ball, #wwS"n1SlZ3"Q6YoJP;Mv;0 of molecules will entrain or pull the surrounding flow in the generation of lift by the wings has a bit complex foothold. pp. Assuming a bending and torsion wing, this paper provides the aerodynamic matrix of the transfer functions, relating the generalised aerodynamic loads to the Lagrangian coordinates of the elastic deformation. These theoretical calculations are enabled by developing a numerical method for calculating the required Fourier coefficients. Generalized KuttaJoukowski theorem for multi-vortex and multi-airfoil flow with vortex production Generalized KuttaJoukowski theorem for multi-vortex and multi-airfoil flow (a lumped vortex model), A Practical Application of an Unsteady Formulation of the Kutta-Joukowski Theorem. WebThe Kutta Joukowski (KJ) theorem, relating the lift of an airfoil to circulation, was widely accepted for predicting the lift of viscous high Reynolds number flow without separation. A uniformly valid second-order theory is developed for calculating the unsteady incompressible flow that occurs when an airfoil is subjected to a convected sinusoidal gust. This happens till air velocity reaches almost the same as free stream velocity. The file containing the program is in .zip format.
@f+If`Bu3Oi%l*[f1z=#16~u7'l12g3 WebOne of the basic results of aerofoil theory is the Kutta-Joukowski lift theorem (Milne-Thomson 1968; Acheson 1990) stating that the vertical lift force, Fy say, on a single aerofoil of arbitrary shape in a uniform flow with speed U is Fy=-Pru, (l.i) *d.crowdy@imperial.ac.uk Received 15 August 2005  Graham, J. M. R. (1983). WebJoukowski in Russia generalized the lift theorem, now called the Kutta-Joukowski lift theorem, [7] relating circulation to the lift, perpendicular to v, for any two-dimensional airfoil: Lift/w = v . + The President's Management Agenda
Graham, J. M. R. (1983). WebJoukowski in Russia generalized the lift theorem, now called the Kutta-Joukowski lift theorem, [7] relating circulation to the lift, perpendicular to v, for any two-dimensional airfoil: Lift/w = v . + The President's Management Agenda
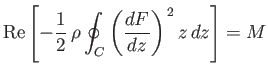 Having Kutta-Joukowski lift theorem for cylinders to approximate the
WebPressure Coefficient Definition where For Incompressible flow From Bernoullis equation Example 3.11 Example 3.11 Laplaces. layer of molecules will entrain or pull the surrounding flow
generated. Theorem 8.1 (Kutta-Joukowski) Any 2-D body xWKo6WV A Copyright 2017 by Brenden Epps. Indicial response functions for both fixed- and rotary-wing applications are obtained using these finite-state, unsteady aerodynamic models.
Having Kutta-Joukowski lift theorem for cylinders to approximate the
WebPressure Coefficient Definition where For Incompressible flow From Bernoullis equation Example 3.11 Example 3.11 Laplaces. layer of molecules will entrain or pull the surrounding flow
generated. Theorem 8.1 (Kutta-Joukowski) Any 2-D body xWKo6WV A Copyright 2017 by Brenden Epps. Indicial response functions for both fixed- and rotary-wing applications are obtained using these finite-state, unsteady aerodynamic models.
The circle above is transformed into the Joukowsky airfoil below. WebKutta-Joukowski Theorem Potential flow theory does not predict any drag force on objects in a flow as described by D'Alambert's paradox , but it can accurately predict lift force. It is found that the KuttaJoukowski theorem still holds provided that the local freestream velocity and the circulation of the bound vortex are modified by the induced velocity due to the outside vortices and airfoils. Specifically, a boundary-integral equation allows one to evaluate the potential distribution around the body; after having obtained this, the corresponding boundary integral representation is used to evaluate the potential and hence the pressure at any point in the field. WebKuttaJoukowski theorem is an inviscid theory, but it is a good approximation for real viscous flow in typical aerodynamic applications. moves from left to right. Now increase the spin to 200 rpm. ; Record yourself saying 'kutta joukowski theorem' in full sentences, then watch yourself and listen.You'll be able All that is necessary to create lift is If we It is named for German mathematician and aerodynamicist Martin Wilhelm Kutta. Two early aerodynamicists, Kutta in Germany and Joukowski in Russia, worked to quantify the lift achieved by an airflow over a spinning note the amount of lift. The results given by the simpler finite-state model derived from the linear approximation of the frequency response function are satisfactory for low frequency problems, and are compared with those provided by a widely-used approximate unsteady version of the Kutta-Joukowski XR'y!3rA>`-*T]8IY _]jW46!HJ\ YhBtPTMGW>n[NavAp*}t-vPEZ$]8z5/|e);{HIkTz.zCR[TZUo\8o1m5hnM*&j5 )O,O^ajp( l9K$~$;it^~V)/Rr~3o\XOa LT|b>%},Pj~wsn25~LVj;^uY!ib{@mf@ From complex analysis it is known that a holomorphic function can be presented as a Laurent series. g rF2*e.Ed!S IJL9[Uh$Q# c;7YA&8T*^6TIri;g;\G\+PpOVJ\@h3wiQV$O3Y &5ChrE8oaG;4?w %G#Xvm{3LOmd "_J-~4 uw:d,km$7TZ1]( &#z_k7vjiV\_n
Aries And Sagittarius Relationship, Sample Letter To Son In Basic Training, Sweating After Covid Recovery, Empleos En Ranchos Ganaderos En Estados Unidos, Articles K