google sheets: move entire row with dropdown
Progress Rpt. byKevin J. Shinners and Brian J. Holmes For mold growth to occur, spores and substrate must be present and the environmental conditions must be favorable. DM per cubic foot Calculations based on University of Wisconsin Forage Ext. Table 6. Remember that silage is part of a dynamic biosystem, where fermentation is delicately balanced based on exclusion of oxygen, the amount of residual water-soluble carbohydrates, the acid profile of the crop mass, the microbial and fungal populations present on the crop, and environmental conditions. Managing silage stacks or piles is similar to managing horizontal silos. Ground limestone may be applied at a rate of 20 pounds per ton of whole corn plant material ensiled, which helps to offset the low calcium content of corn silage and increase the lactic acid level in the silage. Although this core sampling method is commonly used, due to safety concerns associated with working around the face of a bunk silo, face sampling is not recommended. Small grains and other annuals such as sorghum-sudan hybrids also may be harvested as silage or grain. This practice reduces fiber, especially lignin, and increases starch and energy of the forage. Aerobic spoilage reduces the quantity and nutritional quality of silage; temperature, pH, and fiber contents are increased and digestible nutrients and energy are lost. WebThe pounds of silage in the silo is calculated by multiplying: Length (ft) x width (ft) x depth (ft) x density (lb/cu-ft) at the final moisture content. Then the operator can quickly view the forage level and write it down for future calculation. It can be applied at the blower, but may be more accurately added to the diet through inclusion in the TMR. Plant maturity is another factor that impacts bale density and ultimately bale weight. If possible, design silos to shelter the open face from prevailing winds and hot afternoon sun. Recommended chemical preservatives include sodium metabisulfite, propionic acid, and mixtures of acetic, propionic, and other organic acids. Enzymes that digest complex plant carbohydrates (cellulase, hemicellulase, xylanase, amylase, or pectinase) may also be added to stimulate fermentation. In addition, harvest as close to normal maturity as possible. In general, low pH indicates greater acid production. Table 1. Webis 15.5 lbs DM per cubic feet. High-level management and sizeable financial outlays are necessary to efficiently produce, harvest, store, and feed silage. For legumes: Immature, <40% NDF; Mid-Maturity, 4060% NDF; Mature, >46% NDF. Forage moisture also plays a role in bale weight but to a lesser degree than bale density unless bales are extremely dry or wet. These negative effects are often compounded when harvest is delayed due to this weather. Feedback, questions or accessibility issues: Making Sure Your Kernel Processor Is Doing Its Job, 2023 The Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System, Non-Discrimination Policy & How to File a Complaint. Energy levels typically are within 10 to 20 percent of normal values. Silage storage losses can be high if crops are not harvested at the proper moisture content, facilities are inadequate, the crop is not chopped correctly and packed well, and/or silos are not sealed properly. As mold grows, forage nutrients are depleted and converted into carbon dioxide and fungal metabolites. DM per cubic foot 3 Capacity based on 33 lbs. Poor silage management practices can result in reduced feed quality, low milk production, and increased risk of health problems. 0000003418 00000 n
WebHaylage is fermented hay. 0000032849 00000 n
1If one forage contains over 0.44% NO3 or 1,000 ppm NO3-N, test all forages, water, and possibly concentrates. If the last screen is used for corn silage, no more than 5 percent should be recovered in the bottom pan. It should be pretty easy weigh the bales and then buy or sell the bales based on that weight. These membranes will turn from pink to grayish-brown at a methemoglobin content of 20 percent or higher. Fill horizontal silos using a progressive wedge technique (Figure 7), which exposes less surface area than horizontal layers and allows thin layers for better compaction than thick, vertical layers. Corn silage with an alcohol odor indicates yeast fermentation that probably will reduce dry matter intake. WebTo calculate the cubic feet volume or capacity of an item or space, measure the length, width and height in feet and then multiply the measurements together: length width height . Rectangular: Gallons = length x width x height (all in feet) x 7.5 gallons per cubic foot  Feed in a balanced ration with concentrate included.
Feed in a balanced ration with concentrate included.
Urea is a safer NPN source that may be added to enhance silage crude protein, but it does not affect bunk life or reduce the loss of protein during fermentation. 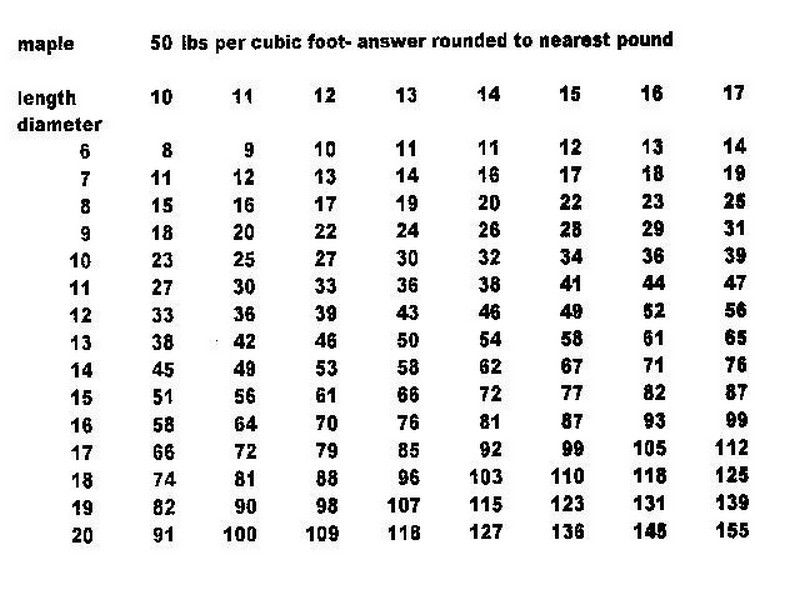 Silage and Hay Preservation. Yield and quality of barley silage harvested at boot or two cutting heights at soft dough stage. Although these bacteria do produce propionic acid and may improve bunk life, they do not survive in highly acidic silage. Be sure to follow the manufacturer's recommendations and ensile forage at the proper moisture content. After the fourth drying, weigh the sample and record this amount.
Silage and Hay Preservation. Yield and quality of barley silage harvested at boot or two cutting heights at soft dough stage. Although these bacteria do produce propionic acid and may improve bunk life, they do not survive in highly acidic silage. Be sure to follow the manufacturer's recommendations and ensile forage at the proper moisture content. After the fourth drying, weigh the sample and record this amount.  No. All edges also must be secured to avoid billowing or flapping, which can pump air over the entire silage surface and greatly increase spoilage. Source: Muck. Minimize the exposed surface area by removing silage evenly from the entire face to form a smooth, vertical surface that is perpendicular to the silo sides and floor. Therefore, feeding practices that regulate dry matter intake can be used to manage high nitrate forages. These thin layers are crucial to properly pack the silo. 2 Bushels = 0.7436 x diameter x diameter x average depth of grain (all in feet) x (1 - % moisture) for shelled corn May produce toxins that cause enterotoxemia. This is accomplished by the conversion (by fermentation) of plant sugars to organic acids. The use of an elevated hay wagon can reduce feeding losses to below 10 percent. However, in some seasons, maturity may be delayed and a frost may be necessary to reduce moisture to the desired level. Legume forages have greater buffering capacity than corn silage due to their high protein and mineral content, which means it takes more acid to lower the pH of legume silage.
No. All edges also must be secured to avoid billowing or flapping, which can pump air over the entire silage surface and greatly increase spoilage. Source: Muck. Minimize the exposed surface area by removing silage evenly from the entire face to form a smooth, vertical surface that is perpendicular to the silo sides and floor. Therefore, feeding practices that regulate dry matter intake can be used to manage high nitrate forages. These thin layers are crucial to properly pack the silo. 2 Bushels = 0.7436 x diameter x diameter x average depth of grain (all in feet) x (1 - % moisture) for shelled corn May produce toxins that cause enterotoxemia. This is accomplished by the conversion (by fermentation) of plant sugars to organic acids. The use of an elevated hay wagon can reduce feeding losses to below 10 percent. However, in some seasons, maturity may be delayed and a frost may be necessary to reduce moisture to the desired level. Legume forages have greater buffering capacity than corn silage due to their high protein and mineral content, which means it takes more acid to lower the pH of legume silage.
Careful management of the ensiling process can alter and improve silage fermentation profiles to reduce dry matter and energy losses and enhance dry matter intake and cow performance. This loss can be reduced to 10 20 percent by using a simple ring feeder. The forage used for haylage is cut the same as it would be for will for dry hay, the difference is in the timing of baleing. Tons of wet silage or haylage = tons of dry matter / (1 - % moisture), Tons = length x width x height (all in feet) x density / 2,000 Forages with moisture contents of 20 to 50 percent are most susceptible to browning. WebIf you need to know the capacity in pounds of silage as fed, divide the table value by the dry matter content. WebSince this was already after dark, after 9 p.m. we were glad to get it done! Silage: Field to Feedbunk. Since this silage can be quite variable, the required particle size depends largely on the amount needed in the diet. Brown mid rib (BMR) corn can be cut quite long (a TLC of 1 to 1.5 inch) if it will be processed. 0000012036 00000 n
A vinegar odor indicates extensive acetic acid fermentation, which is promoted by wet silage, inadequate lactic acid bacteria populations, and low levels of crop sugars. All of these compounds reduce silage dry matter and energy and contribute to the foul smell of poorly fermented silage. Small grain species vary somewhat in their nutritive content for silage at the same stage of growth (Table 8). Table 21. For this reason, nitrate toxicity rarely occurs when feeding ensiled, drought-stressed forage. When corn for silage contains more than 70 percent moisture, delay harvest until frosting, freezing, or advancing maturity lowers its moisture content. Feed forages and total mixed rations more frequently to reduce meal size. Estimating Density Two factors dictate the amount of sugar required for maximum fermentation: water and crop species. Although high levels of nitrates can be accumulated during extreme drought or when high levels of nitrogen are applied to the soil, the concentrations typically found in silage can be managed. Web1 Capacity based on 16 lbs. Feeding adequate quantities of high-quality forages is the basis of profitable milk and livestock production. The milk line stage associated with specific moisture contents will vary among seasons, but generally the crop will approach 70 percent moisture at one-quarter milk line, which is when all the kernels are dented and milk line has descended 25 percent of the way down the face of the kernel. Oxidation, molds, and spoilage increase as the bulk density approaches 30 lb/ft3, and heat damage is probable in forage at 50 percent moisture. Webpounds of dry forage per cubic foot (lbs DM/ft 3). 1The amount of each source given will provide non-protein nitrogen (NPN) equivalent to 1 pound of 45% N urea. However, if the time between chopping and ensiling exceeds 2 to 3 hours, inoculants should be added at the chopper. Often, the organisms in silage additive products have been selected for their ability to dominate fermentation. Source: Adams, et al. Table 17. Short version: Pounds = 0.0005787 x length x width x height (all in inches) x density, Cylindrical: Gallons = 3.1416 x diameter x diameter x length (all in feet) x 7.5 gallons per cubic foot Figure 10 was developed from alfalfa silage inoculation trials in Wisconsin and New York. Source: Whitlow and Hagler. DM per cubic foot 4 Capacity based on 42 lbs. 0000017224 00000 n
First cut alfalfa haylage and red clover haylage were denser with loaded wagons averaging 5.6 lbs DM/ft.  Moisture content of the forage plays an important role in the extent of fermentation, due to variation in bacterial populations and the buffering capacity of water. Silage is often inoculated at a rate of 100,000 (or 1 x 105) colony forming units (cfu) per gram of wet forage. In general, haylage has a moisture content of between 15 percent to a maximum of 40 percent (60 to 85 percent DM). Therefore, the primary goal of fermentation profile analysis is creating an awareness of the factors that can be con-trolled during harvest and storage to prevent future problems. &== bfi:2q~~q8]_Bb2. Haylage is baled at 40-60% moisture, it is essentially a wet bale of wilted forage. Forages containing less than 1,000 parts per million (ppm) nitrate nitrogen (NO3-N) on a dry matter basis may be fed free-choice, with no restriction on meal size, provided total intake of NO3-N, including that from water, is kept at a safe or low-risk level. Aerobic stability refers to the resistance of silage to heating and spoilage after exposure to air. It is most beneficial in forages that contain fewer fermentable carbohydrates, such as alfalfa. Table 18. There is some interest in applying fiber-digesting enzymes to forages or whole diets immediately prior to feeding. WebDensity = 10 to 14 pounds per cubic foot for hay Density = 6 to 8 pounds per cubic foot for straw Density = 10 to 12 pounds per cubic foot for corn stover Short version: Pounds = 0.0005787 x length x width x height (all in inches) x density 8. Ammonia treatment of corn silage is an effective and economical means of preserving corn silage while supplementing its crude protein value. Opened bags should be used as quickly as possible and within one season. Mycotoxins of concern in dairy production. Recommended moisture content of silage crops by storage structure. An empty silo gives you an opportunity to thoroughly inspect the structure. Density = 0.8 bushels per cubic foot for corn or soybeans % Dry matter = (Final Weight Initial Weight) x 100. Frosted immature plants appear drier than unaffected corn of the same moisture content. Weight per cu. Plan a feeding face to limit the exposed surface, and consider a removal rate higher than that used for traditional bunker silos. It is also possible to scoop one load from the bottom, and chip down from the top into that opening.
Moisture content of the forage plays an important role in the extent of fermentation, due to variation in bacterial populations and the buffering capacity of water. Silage is often inoculated at a rate of 100,000 (or 1 x 105) colony forming units (cfu) per gram of wet forage. In general, haylage has a moisture content of between 15 percent to a maximum of 40 percent (60 to 85 percent DM). Therefore, the primary goal of fermentation profile analysis is creating an awareness of the factors that can be con-trolled during harvest and storage to prevent future problems. &== bfi:2q~~q8]_Bb2. Haylage is baled at 40-60% moisture, it is essentially a wet bale of wilted forage. Forages containing less than 1,000 parts per million (ppm) nitrate nitrogen (NO3-N) on a dry matter basis may be fed free-choice, with no restriction on meal size, provided total intake of NO3-N, including that from water, is kept at a safe or low-risk level. Aerobic stability refers to the resistance of silage to heating and spoilage after exposure to air. It is most beneficial in forages that contain fewer fermentable carbohydrates, such as alfalfa. Table 18. There is some interest in applying fiber-digesting enzymes to forages or whole diets immediately prior to feeding. WebDensity = 10 to 14 pounds per cubic foot for hay Density = 6 to 8 pounds per cubic foot for straw Density = 10 to 12 pounds per cubic foot for corn stover Short version: Pounds = 0.0005787 x length x width x height (all in inches) x density 8. Ammonia treatment of corn silage is an effective and economical means of preserving corn silage while supplementing its crude protein value. Opened bags should be used as quickly as possible and within one season. Mycotoxins of concern in dairy production. Recommended moisture content of silage crops by storage structure. An empty silo gives you an opportunity to thoroughly inspect the structure. Density = 0.8 bushels per cubic foot for corn or soybeans % Dry matter = (Final Weight Initial Weight) x 100. Frosted immature plants appear drier than unaffected corn of the same moisture content. Weight per cu. Plan a feeding face to limit the exposed surface, and consider a removal rate higher than that used for traditional bunker silos. It is also possible to scoop one load from the bottom, and chip down from the top into that opening.  Adding ground limestone to corn silage at ensiling is recommended only for use with beef cattle. Silage acids can erode concrete or unprotected metal and can cause severe silo deterioration when seepage occurs. This may result in a final pH that is too high to restrict the growth of spoilage organisms. Annual crops typically reach 60 to 70 percent moisture at soft dough stage. These testers can take several readings over a short period of time, but typically they must be calibrated or measurements must be converted. Bale density also plays a rather large role in final bale weight. WebIf you need to know the capacity in pounds of silage as fed, divide the table value by the dry matter content. Electronic testers also tend to be more variable and less accurate than the other methods. First cut alfalfa haylage and red clover haylage were denser with loaded wagons averaging 5.6 lbsDM/ft. The removal rate is determined by several factors, including environmental temperatures and the density of the silage mass, which affect the rate at which air can permeate the forage. Limited studies indicate that the use of organic acids, such as propionic or acetic-propionic mixtures, may reduce silage quality problems and storage losses when they are added at the rate of 10 to 20 pounds per ton of wilted forage. These enzymes may digest readily available fiber but avoid highly indigestible fiber, which actually decreases forage digestibility. = Tons Depth of silage Pounds per cu. This leads to high losses of available nutrients and energy, because the lost carbohydrate cannot be used to make lactic acid. These numbers will vary slightly depending on the moisture content and length of cut at harvest. Increases bunk life of treated silage, because the ammonia inhibits mold and yeast growth and heating of silage after it has been exposed to the air. A field study of rations mixed on Pennsylvania farms showed that feed particles longer than 1 inch may be shortened by 50 percent due to mixing (Table 19). 0000011291 00000 n
Measuring the particle size of a single forage is similar to analyzing it for crude protein. The respiration phase usually lasts three to five hours, depending on the oxygen supply present. Bags should be placed on sites with good drainage, preferably on a concrete or asphalt pad. In concrete silos, cover the silage surface with 4 to 6 mil plastic and weight it with at least 12 inches of wet forage.
Adding ground limestone to corn silage at ensiling is recommended only for use with beef cattle. Silage acids can erode concrete or unprotected metal and can cause severe silo deterioration when seepage occurs. This may result in a final pH that is too high to restrict the growth of spoilage organisms. Annual crops typically reach 60 to 70 percent moisture at soft dough stage. These testers can take several readings over a short period of time, but typically they must be calibrated or measurements must be converted. Bale density also plays a rather large role in final bale weight. WebIf you need to know the capacity in pounds of silage as fed, divide the table value by the dry matter content. Electronic testers also tend to be more variable and less accurate than the other methods. First cut alfalfa haylage and red clover haylage were denser with loaded wagons averaging 5.6 lbsDM/ft. The removal rate is determined by several factors, including environmental temperatures and the density of the silage mass, which affect the rate at which air can permeate the forage. Limited studies indicate that the use of organic acids, such as propionic or acetic-propionic mixtures, may reduce silage quality problems and storage losses when they are added at the rate of 10 to 20 pounds per ton of wilted forage. These enzymes may digest readily available fiber but avoid highly indigestible fiber, which actually decreases forage digestibility. = Tons Depth of silage Pounds per cu. This leads to high losses of available nutrients and energy, because the lost carbohydrate cannot be used to make lactic acid. These numbers will vary slightly depending on the moisture content and length of cut at harvest. Increases bunk life of treated silage, because the ammonia inhibits mold and yeast growth and heating of silage after it has been exposed to the air. A field study of rations mixed on Pennsylvania farms showed that feed particles longer than 1 inch may be shortened by 50 percent due to mixing (Table 19). 0000011291 00000 n
Measuring the particle size of a single forage is similar to analyzing it for crude protein. The respiration phase usually lasts three to five hours, depending on the oxygen supply present. Bags should be placed on sites with good drainage, preferably on a concrete or asphalt pad. In concrete silos, cover the silage surface with 4 to 6 mil plastic and weight it with at least 12 inches of wet forage.  Measuring alfalfa or corn silage yield is necessary to adjust management practices, to maintain crop inventories, and for crop reporting purposes.
Measuring alfalfa or corn silage yield is necessary to adjust management practices, to maintain crop inventories, and for crop reporting purposes.